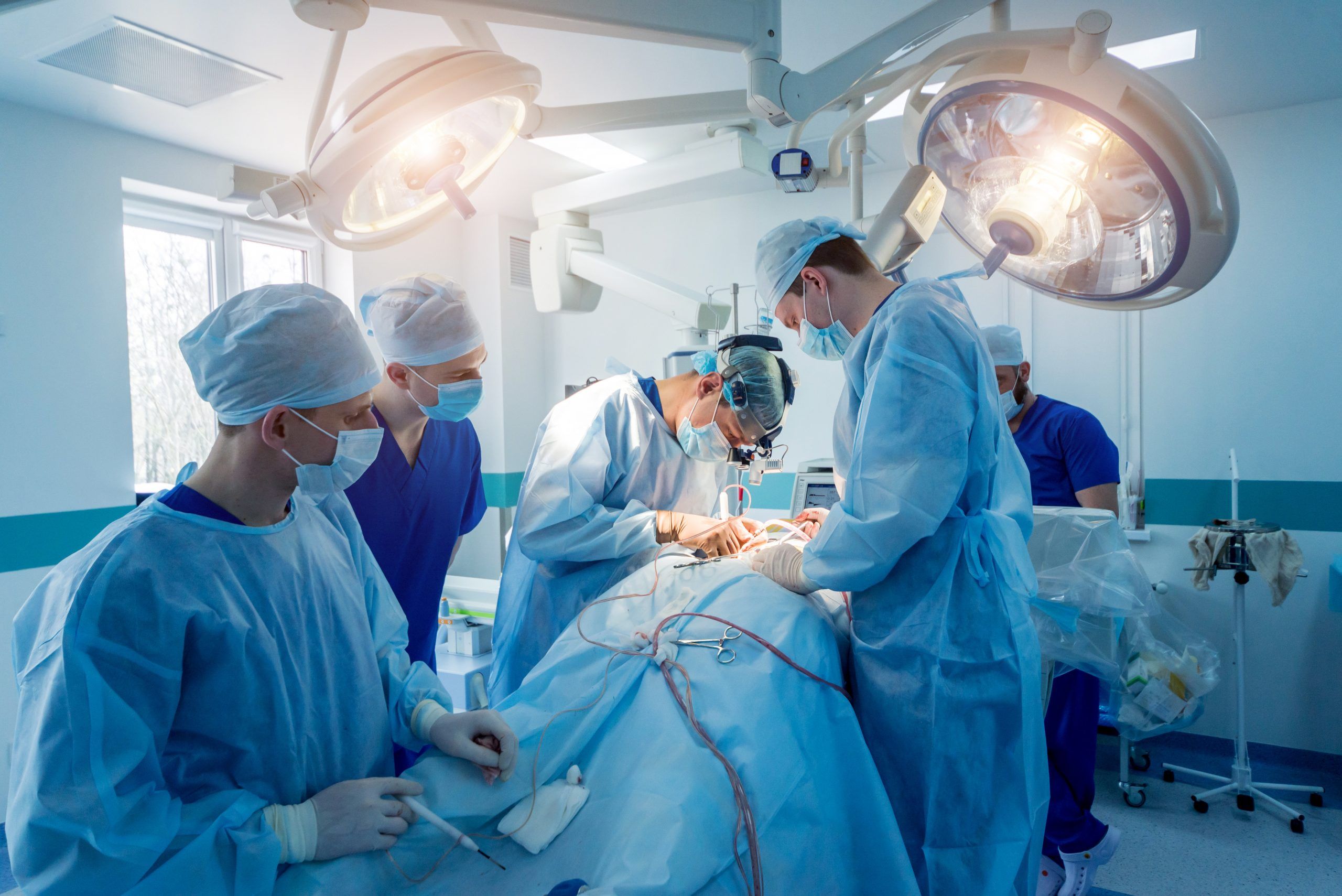
Surgical Treatments
- Hernias: abdominal hernia, inguinal hernia, umbilical hernia, eventrations (open or laparoscopic)
- Esophagogastric surgery: hiatus hernia, gastroesophageal reflux, tumors
- Intestinal surgery: tumors, polyps, diverticula, hernias, appendicitis
- Proctological surgery: hemorrhoids, perianal fistulas, anal fissure, perianal abscess, pilonidal cyst-fistula
- Liver, bile duct and pancreas surgery, tumors, cysts
Laparoscopy (cholecystectomy, hiatal hernia, stomach, diverticulitis, pancreatic disease, liver surgery) - Breast surgery: benign lesions
- Soft tissue surgery: benign lesions, cysts, lipomas
- Endocrine surgery: thyroidectomy, parathyroid gland surgery, adrenal gland
- Bariatric surgery: gastric tube, gastric bypass, gastric band, gastric balloon
- Biopsies, lymph node removal
Frequent surgical pathologies
- Hernias: A hernia is the prolapse of any organ or tissue outside the cavity in which it is normally housed. The most common hernias develop through the abdominal wall, through natural or artificial gaps that constitute weak points in the abdominal wall, which begins the process of hernia formation. Inguinal hernia: Usually a part of the intestine that prolapses out through a weakened place in the abdominal muscles. There can be major complications such as obstruction or strangulation of the herniated intestinal part. In symptomatic, large or complicated hernias, surgical treatment is indicated. Abdominal hernia: An abdominal hernia occurs in the midline of the abdomen, in the umbilical area or in a previously operated area where the scar presents the weak point of the abdominal wall. Given the risk of significant complications, surgical treatment of these hernias is recommended.
- Appendicitis: Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small protrusion of the ascendens colon that projects into the lower right side of the abdomen. As the inflammation progresses there are more symptoms (pain, nausea, vomiting, fever). Treatment consists of surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy).
- Gallstones: Gallstones are deposits of concentrated bile that form in the gallbladder. Two types of stones are differentiated according to their main content: cholesterol or bilirubin stones. In case of a symptomatic pathology (pain, nausea, vomiting) removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is indicated.
Make an appointment























